Inputs and outputs
In the previous module you came up with the pin numbering scheme and identified power and ground. Now we'll go a little deeper to figure out data flow.
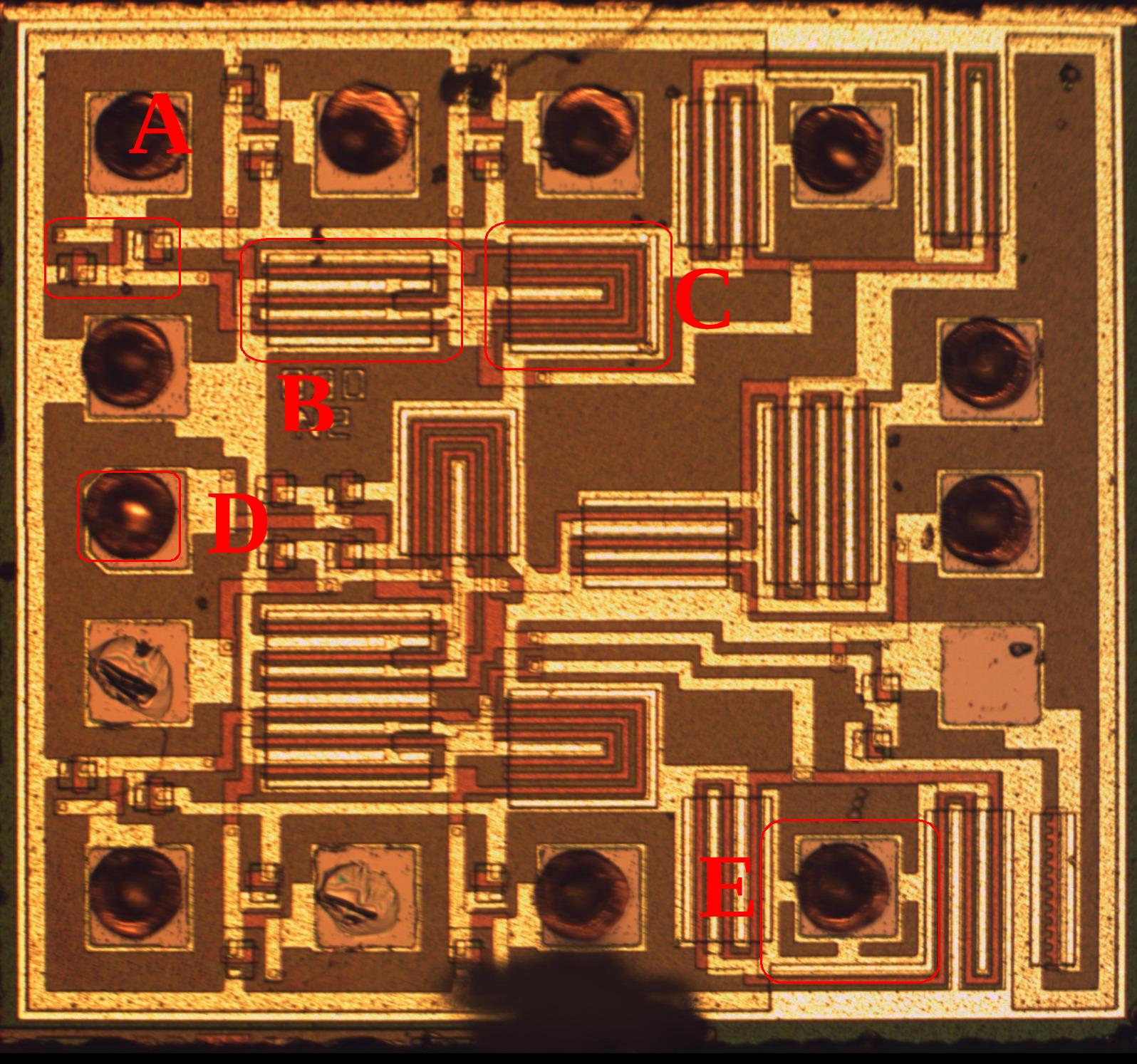
- Identify the circle containing ESD protection
- Detail
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- [1]
- (1)
- Many chips use large parallel diodes for ESD protection and so this ones a little different. However, ESD protection can often be identified by virtue of a component that attaches to both VDD and VSS. While some of the transistors do this, they have logical connections that indicate they have a higher purpose. ESD protection on the other hand tends to be very simple and regular. Looking at the components in A I believe they are resistors as seen with NMOS logic (ex: see Intel 4004 die photos and Flylogic analysis). Presumably this provides a more favorable conductive path and shunts away from the input gates.
- B is a transistor
- C is a transistor
- D is a bond wire (ball bond)
- E just has more metal and metal doesn't typically help ESD. It can on larger chips when its used as a capacitor between VDD and VSS
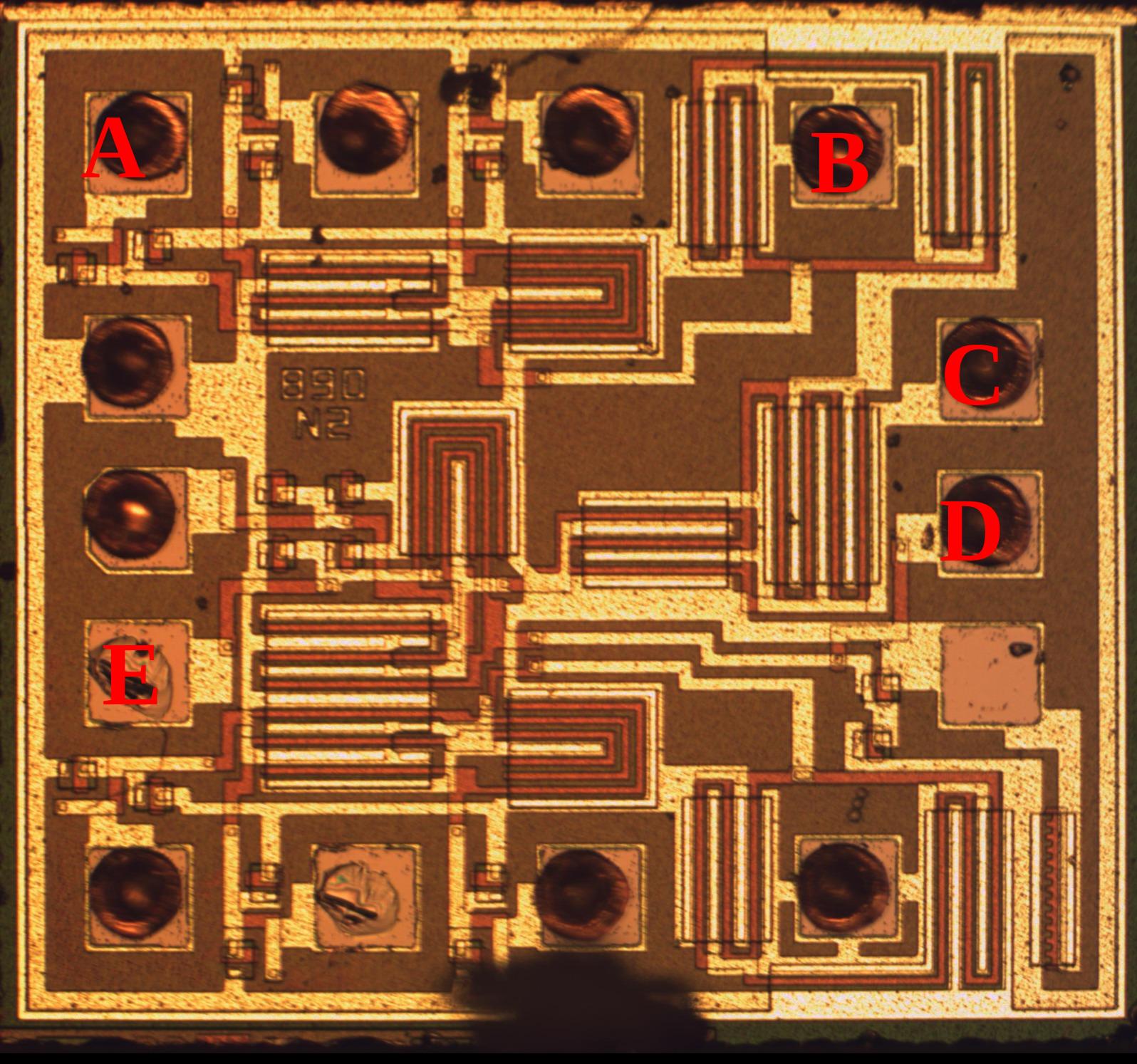
- Identify inputs
- Detail
- ie not outputs or power/ground
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- [1|4|5]
- (1)
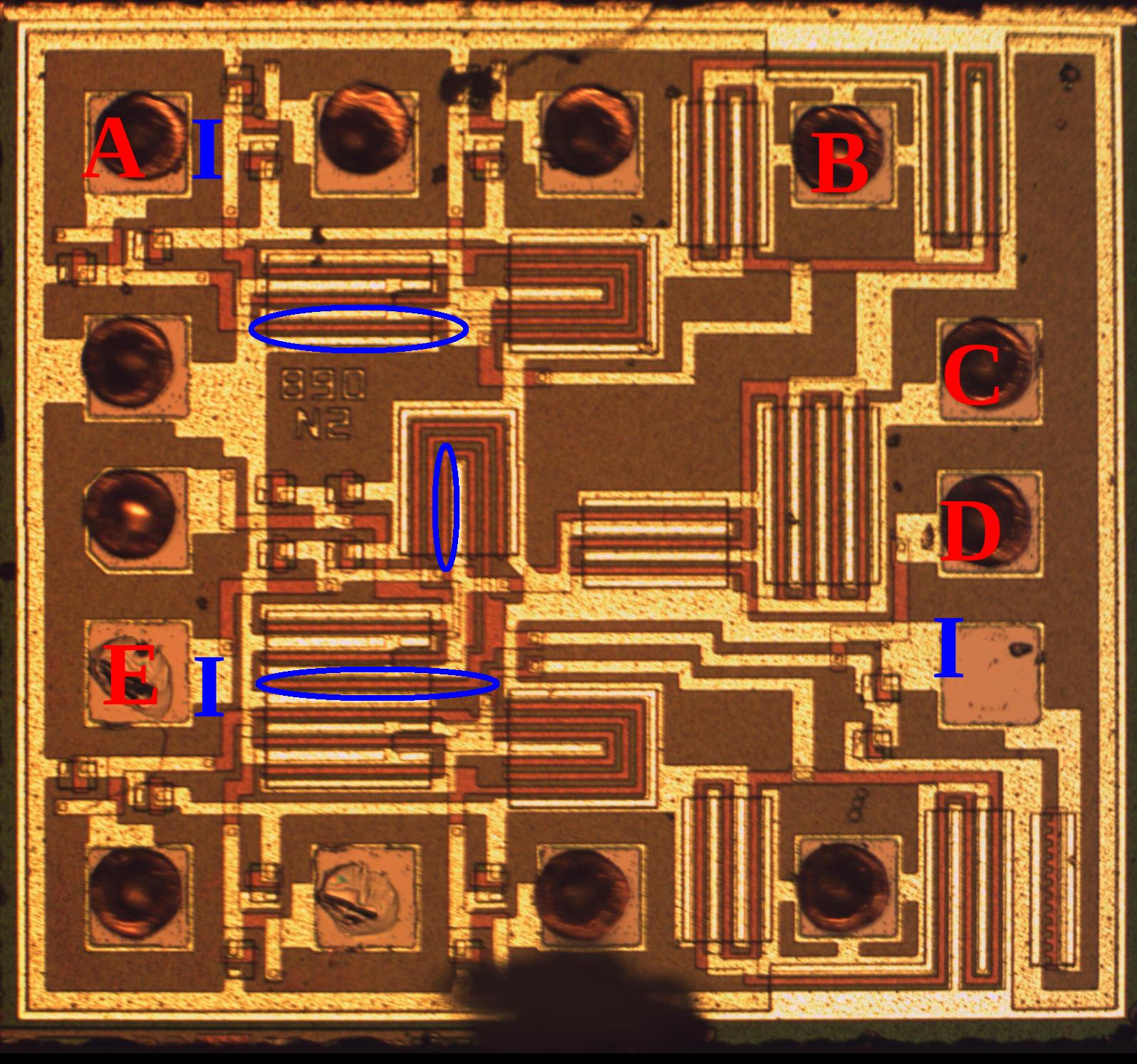
- Anything with a fat transistor near the pad not connected to a gate is a pretty clear output or possibly tri-state. I highlighted a gate on each questioned input, although keep in mind that simply having a gate attached to a pin doesn't make it an input as the circuit can have feedback or tri-state (necessary but not sufficient). Going through each pin you see that each is either connected to only gates or only source/drain. We can now identify all pins as either power, input or output. D had to be traced to the other side of the die and is the lowest circled gate.
Except where otherwise noted, content on this wiki is licensed under the following license: CC Attribution 4.0 International